
Usually, you will recognize atrial flutter by consistent saw-tooth or wave-like pattern between the QRS complexes. VT can have rates more than 240 but in this situation, the patient will most likely be pulseless, and you will treat using the cardiac arrest algorithm. Symptoms will be seen when the ventricular rate is affected or if the patient develops a blood clot due to the pooling of blood in the atria related to the ineffective fluttering. The ventricular rate may still be relatively low but usually more than 100. Remember that flutter will many times only affect the atrial rate. Are there any other rhythms that have rates that high? If not that might be one way to help identify flutter when not a sawtooth pattern.Ī: Atrial flutter does not always have such a high atrial rate, but it usually will. Q: I would assume that atrial flutter always has a rate more than 240. Studies have shown that lower doses between 20-50 J are adequate for the conversion of atrial flutter. The page which states that 20-50 J can is used for the conversion of atrial flutter is speaking about atrial flutter in general and this could mean both stable and unstable atrial flutter. Synchronized cardioversion is indicated, and the starting dose for narrow, regular tachycardia would be 50 J. Q: Energy levels for cardioversion of unstable a-flutter with both biphasic and monophasic devices? I haven’t seen anything as low as 20-50 joules mentioned in the AHA material, but I’m just getting started.Ī: Unstable atrial flutter is treated as an unstable tachycardia within the tachycardia algorithm. You would want to perform a TEE to ensure that there is no thrombus formation and you would want to initiate anticoagulation therapy.

Q: What are the chances of the formation of thrombus in the atrial cavity in the case of long-standing atrial flutter? Do we have to give anticoagulation, as in atrial fibrillation, to minimize the risk of emboli?Ī: The chances for thrombus formation are relatively high. (3.84 mb)Ĭlick for next Rhythm Review: Atrial Fibrillation Questions Asked On This Page Please allow several seconds for the video to load. 20-50J is commonly enough to revert to sinus rhythm.ĪHA recommends an initial shock dose 0f 50-100 J for cardioverting unstable atrial flutter.īelow is a short video which will help you quickly identify atrial flutter on a monitor. CardioversionĪtrial flutter is considerably more sensitive to electrical direct-current cardioversion than atrial fibrillation, and usually requires a lower energy shock. Drugs are not used to manage unstable tachycardia. When atrial flutter produces hemodynamic instability and serious signs and symptoms, it is treated using ACLS protocol.įor the patient with unstable tachycardia due to this tachyarrhythmia (atrial flutter), immediate cardioversion is recommended. Treatmentįor the purposes of ACLS, atrial flutter is treated the same as atrial fibrillation. Prevent complications from atrial flutter with early cardioversion. Ineffective atrial contractions can lead to thrombus formation in the atria and rapid ventricular rates can cause decompensation and heart failure. These complications are usually due to ineffective atrial contractions and rapid ventricular rates.

These rapid atrial rates are caused by electrical activity that moves in a self-perpetuating loop within the atria.
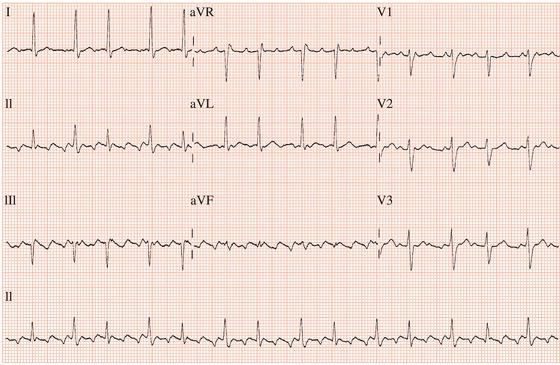
Atrial flutter is typically not a stable rhythm and will frequently degenerate into atrial fibrillation.Ītrial Flutter will usually present with atrial rates between 240-350 beats per minute. Atrial flutter is an abnormal heart rhythm that technically falls under the category of supra-ventricular tachycardias.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
